Bone marrow transplantation
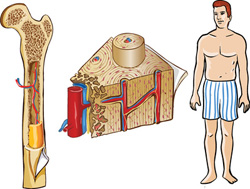
Bone marrow transplantation - is used as a therapeutic procedure for a number of cancers, such as acute myelogenous leukemia, acute leukemia in relapse, lymphoma and other cancers. This treatment can cure the most of severe cancer forms.
The purpose of a bone marrow transplant is to assure success of the high doses chemo-- and radiotherapy, when treatment with lower doses are useless.
Thus, a bone marrow transplant makes it possible to use very high doses of chemotherapy and radiation to kill cancer cells in the body with negative side effect-- the destruction of their own bone marrow that produces hematopoietic cells. Procedures below are described replanting of healthy bone marrow cells that restores the ability of their hematopoietic function.
Types of bone marrow transplantations:
- Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation when used bone marrow of another person - the donor.
- Autologous bone marrow transplantation when used bone marrow or stem cells of the patient.
Bone marrow is taken and stored frozen until to treat patient. For this, bone marrow is harvested from the femurs patient or a donor.

After completion of phase of chemotherapy combined with or without radiotherapy, the stored bone marrow injected back into the body (transplanted) using an intravenous method.
Bone marrow transplantation has been used successfully as a standard therapeutic procedure for treatment of a bone marrow cancer as well as other cancers, which required treatment with a very high-dose chemotherapy in combination radiation treatments.
For allogeneic bone marrow transplantation, it is necessary that donor and recipient must be immunologically identical. For most people the most suitable donors are brothers and sisters. The probability of matching bone marrow in this case is 1:4. Identical twins have identical HLA – the major histocompatibility complex factor in the human. The system includes a gene region on chromosome 6 that encode the HLA-antigens involved in the different reactions of immune response.
Bone marrow transplantation. Stages of the procedure.
As a first necessary step, it is imperative to complete chemotherapy and \ or radiotherapy to achieve a maximum possible destruction of cancer tissue. During the intensive therapy, a patient is constantly medicated to prevent nausea and vomiting and to maintain the water-salt balance, and if necessary is treated with the sedatives drugs. Patients who is undergoing bone marrow transplantation, must be in remission, since the weakening disease symptoms most likely will enhance effect of the severe treatment. However, the chemo- and radiation therapies can be successful in the presence of small amounts of cancer cells as well.
Removing the marrow from the patient or the donor occurred under general anesthesia. Up to 1 liter of bone marrow can be harvested from a number of points over the hip and breast bones using special syringe. The procedure requires a brief hospitalization of the donor to carefully monitor his/her condition, as is the following procedure may cause the patient''s pain and unpleasant feeling of weakness. Treatment of anti-cancer drugs, infusion fluids, blood sampling and bone marrow transplantation is usually performed via the central catheters.
Bone marrow injected using a drop method via a central catheter, like blood transfusion, and delivered through the bloodstream to the bones. Usually, a normal hematopoiesis is restored only after several weeks, during which the patient carefully monitored.
After discharge, the patient remains under the close supervision of the physician-hematologists.
Professor Arnon Naglar-Chairman of the Department of Hematology, Bone Marrow Transplantation and The Blood Bank. He is an international expert on stem cell transplantation, harvesting and banking bone marrow, immunotherapy, cancer vaccination. |
 |



