Tumors of the brain and nervous system (brain cancer)
Diagnosis of brain tumors
It is important to diagnose brain cancer at the initial stage of the disease when the tumor is still small, and neurosurgical assistance is most effective.
The Department of Neurosurgery at the Hospital Tel-Ha- Shomer uses a large set of visual, physiological and laboratory examinations:
- A detailed neurological examination.
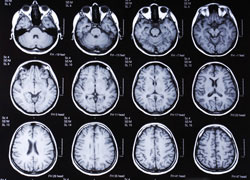
- CT (computed tomography)
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), nuclear medicine techniques
- Electroencephalography (EEG) - the identification of focal disorders of the brain biopotential, assessing disease severity of the brain as a whole.
- Radiography - identification of secondary signs of increased intracranial pressure, as well as detection of local changes in the bones of the skull that can result from brain cancer.
- Ultrasound - performed for children with open fontanel. Good quality diagnosis, including prenatal.
- Lumbar (spinal) puncture is performed to measure the pressure and laboratory analysis of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Positron emission tomography (PET) - a survey in which a certain amount of radioactive fluoride and glucose is injected into the veins to determine the extent of accumulation of glucose into the tumor and normal tissues. High malignancy tumor absorbs more glucose than normal tissue of the brain and spinal cord. Tumors of low-grade accumulate less sugar than normal tissue. PET method is also used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment, and it also gives an opportunity to distinguish scar tissue from residual tumor tissue.
- Angiography. The method is used to assess blood supply of the tumor using a contrast medium injected into a vein or artery. The result of the procedure helps to optimally plan the operation.
- Biopsy. The final diagnosis is established only after microscopic examination of a suspicious area in the tumor tissue removed during surgery.
Prognosis of brain cancer depend on tumor grade, size and localization
Risk factors that contribute to the brain and spinal cord tumors are:
- Environment – Such as radiation
- Disorders of the immune system, innate, result of treatment for other tumors, as well as prophylactic treatment with drugs suppressants of the immune system. People with altered immune systems have an increased risk of lymphoma of the brain and spinal cord.
- Family history. The presence of family history of multiple cases of brain and spinal cord.
- Heredity. For example, neurofibromatosis type 2 is a genetically transmitted disease
Brain cancer. Can it be diagnosed early?
Currently, special methods of screening for early diagnosis of tumors of the brain and spinal cord do not exist. A responsible attitude to the changes in the health of those exposed to the above risk factors for cancer, however, will have a largely positive impact on your health.
What are the symptoms of brain and spinal cord?
Change the neurological picture - in some cases, these symptoms may occur suddenly. Such symptoms may include numbness and weakness of the lower extremities, headache, nausea, vomiting, the appearance of sheet in the eyes, double vision subjects. The headache is seen in 50% of patients.
The main types of tumor formation of the central nervous system
- Brain stem glioma
- Astrocytic tumors of pineal region
- Piloidnaya astrocytoma
- Diffuse astrocytoma
- Anaplastic astrocytoma
- Glioblastoma
- Oligodendroglial tumors
- Mixed glioma
- Ependymal tumors
- Medulloblastoma
- Parenchymal pineal tumors
- Meningeal tumors
- Germ cell tumors
- Craniopharyngiomas
- Relapse of adult brain tumors
- Metastatic brain tumors
- Cerebellar astrocytoma
Dr Jacob Baram, Head of Department.
|
 |



